The concept of “biocentrism debunked,” which says that life created the cosmos and that all life is associated with it rather than the other way around, has been gaining ground rapidly in some circles. This viewpoint emphasizes how important biology and living things have been in helping us comprehend the universe.
However, despite the appeal of Biocentrism Debunked to many, it is essential to subject these ideas to thorough examination from both scientific and philosophical perspectives, as they may face challenges from various angles.
What Is Biocentrism Debunked?
The term “Biocentrism Debunked” from American scientist Robert Lanza gives a novel perspective.This perspective holds that mind is the primary element of the universe, and all other elements, including matter, are its byproducts.
The universe is viewed as a mental construct rather than a tangible thing in Biocentrism Debunked.According to this perspective, our views of the universe are shaped via the lens of our own awareness rather than being based on objectivity.
Supporting Arguments for Biocentrism Debunked

Biocentrism Debunked Garner’s support through several compelling arguments, chief among them being its capacity to elucidate the enigmatic phenomenon of consciousness.
Conventional physical theories, including materialism and dualism, have consistently fallen short in elucidating the origin of consciousness. Biocentrism Debunked posits that consciousness serves as the bedrock of the universe, thereby offering a rationale for our conscious existence.
Furthermore, another argument bolstering biocentrism examples is its ability to account for the intricate fine-tuning of the cosmos. The universe conspicuously exhibits a remarkable alignment conducive to the sustenance of life, and biocentrism definition posits that this remarkable harmony arises from life and consciousness being the very underpinnings of the cosmos.
In the biocentric perspective, the universe transcends mere happenstance and randomness; rather, it emerges as a sophisticated system that has evolved purposefully to facilitate life’s existence.
Challenges to the Biocentrism Debunked Theory
Biocentrism Debunked Theory proposes a perspective in which space and time are considered products of human cognition, implying that our understanding of these concepts is tools created by sentient beings rather than objective, external realities. However, this standpoint faces contradictions with well-established scientific observations and theories.
For instance, various experiments and phenomena, such as gravitational lensing and time dilation, have provided empirical validation for Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity. This theory forms the foundation of our contemporary comprehension of space and time. Moreover, events in the cosmos that predate the emergence of life provide evidence that space and time persist independently of observers.
Another facet where biocentrism definition theory encounters criticism is its assertion that life and consciousness possess a fundamental status in the universe. While life and consciousness are undoubtedly remarkable phenomena, equating them to fundamental forces like gravity or electromagnetism lacks empirical substantiation. Unlike quantifiable and universally observable forces like gravity, consciousness remains a subjective experience that cannot be measured in the same manner as physical forces.
Can Biocentrism Debunked Act as a Catalyst for Environmentalism?
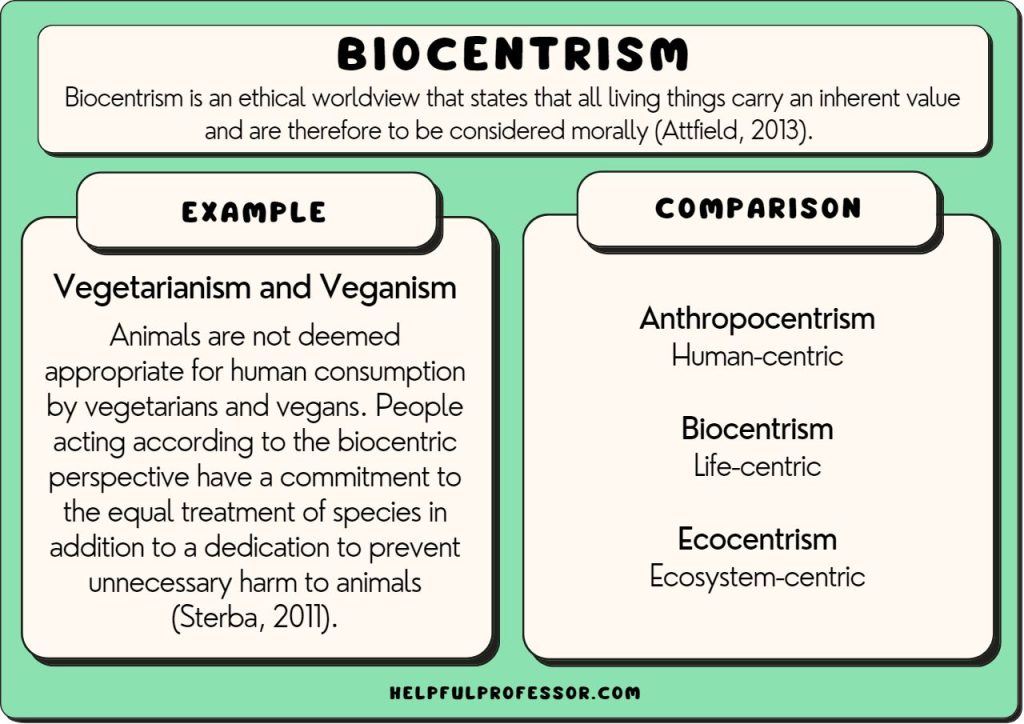
Biocentrism Debunked, as a philosophical perspective within the realm of environmental ethics, posits that every living organism, not just humans, possesses an inherent moral worth. This refined philosophy champions the rights and significance of all living entities, advocating for the protection of individual organisms’ survival, and it is deeply rooted in the principle of individualism.
In contrast, holistic environmental ethics, often exemplified by concepts like “land ethics,” which is termed ecocentrism, argues that entire species and ecosystems hold greater moral importance. These holistic ethical viewpoints prioritize the well-being of species and ecosystems in moral deliberations.
Although Biocentrism Debunked and ecocentrism have different theoretical underpinnings, it is possible and necessary for these two ideologies to converge in terms of environmental ethics. The creation of an ethical framework that encourages peaceful cohabitation between people and the natural environment ought to be the ultimate aim. By extending human morality to include all living things and the environment, both ideologies pave the way for the formation of a global environmental ethic based on their shared logical precepts.
In the world of environmental ethics, biocentric ideology asserts that all forms of life inherently possess a “good,” suggesting an extension of moral recognition to include non-human life forms. This encompasses various strands of thought, such as Schweitzer’s ethic of reverence for life, Peter Singer’s ethics of animal liberation, and Paul Taylor’s bio-egalitarianism.
Three fundamental principles underpin this philosophy: First, all living entities have an inherent drive to counteract the natural process of entropy, preserving their organization and ensuring their survival and integrity. Second, self-preservation is a universal objective for all life forms, making it an intrinsic value and “good.” Lastly, despite the diverse ways in which life forms organize and survive, their inherent values are inherently equal. As a result, they deserve equal moral rights, demanding moral recognition, consideration, and protection.
Is Biocentrism Debunked?
Although the biocentrism definition presents an intriguing outlook on the universe, it has not gained widespread acceptance within the scientific community. The theory has not demonstrated the ability to formulate testable predictions and lacks empirical substantiation.
Furthermore, it relies on an erroneous interpretation of physics, further eroding its credibility.
Conclusion
Biocentrism Debunked posits that consciousness serves as the fundamental basis of the universe. Though it presents a thought-provoking viewpoint on the cosmos, it lacks widespread acceptance within the scientific community.
The theory struggles to yield consistent predictions or furnish empirical substantiation. While Biocentrism Debunked may possess philosophical significance, its status as a bona fide scientific theory remains questionable at present. Nevertheless, the investigation of novel concepts and theories constitutes a crucial facet of the scientific endeavor, and scrutinizing biocentrism examples could potentially pave the way for fresh perspectives and revelations in the future.
FAQs
Who Proposed the Concept of Biocentrism Debunked?
The concept of Biocentrism Debunked was initially put out by American scientist Robert Lanza in 2007. It was via Lanza’s book, “Biocentrism Debunked: How Life and Consciousness Unlock the Secrets of the Universe,” that this theory became well known.
Is Biocentrism Disproven Still Considered a Reliable Scientific Theory?
As of the current understanding, Biocentrism Debunked does not hold the status of a validated scientific theory. While it offers an intriguing perspective on the nature of the universe, it has not garnered empirical support or produced testable predictions.
What Are the Ramifications of Embracing Biocentrism Debunked?
Our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it would be profoundly affected if Biocentrism Debunked were to be supported as a factual foundation. It would imply that the most fundamental features of the cosmos are life and awareness, with everything else playing a supporting role.



